
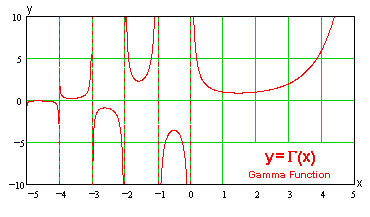
Tablas Matemáticas de David: Función Gamma  |
| (Matemática | Cálculo | Integrales | Funciones Especiales | Función Gamma) |

 (x) = (x) = 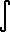  e -t t(x-1) dt e -t t(x-1) dt |  (x) = rx (x) = rx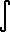  e -rt t(x-1) dt e -rt t(x-1) dt |
 (x) = 2 (x) = 2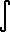  e(-t^2) t(2x-1) dt e(-t^2) t(2x-1) dt | (  (x) (x) (y) ) / ( (y) ) / (  (x) + (x) +  (y) ) = Beta(x,y) (y) ) = Beta(x,y) |
 (x+1) = x (x+1) = x  (x) (x) |  (x+1) = x! (x+1) = x! |
 (0+) = + (0+) = +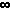 |  (1/2) = (1/2) = 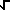 (PI) (PI) |
 (z) (z)  (1-z) = PI csc(PI z) (1-z) = PI csc(PI z) |  '(1) = - gamma (el '(1) = - gamma (el 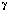 constante de Euler = 0.577215...) constante de Euler = 0.577215...) |
 '(x) = '(x) =  (x) lim (n--> (x) lim (n-->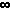 ) [ ln(n) - ) [ ln(n) - 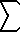 (k=0..n-1) 1/(x+k) ] (k=0..n-1) 1/(x+k) ] | |
Expansiones de la Función  | ||
| ||
La Serie Asintótica del Stirling (x+1) = (x+1) = 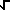 (2PIx) xx e -x { 1 + 1/(12x) + 1/(288 x2) - 139/(51840 x3) - 571/(2488320 x4) + 163879/(209018880 x5) + 5246819/(75246796800 x6) - 534703531/(902961561600 x7) - ...} (este solamente es una aproximación. Ver nota (en inglés).) (2PIx) xx e -x { 1 + 1/(12x) + 1/(288 x2) - 139/(51840 x3) - 571/(2488320 x4) + 163879/(209018880 x5) + 5246819/(75246796800 x6) - 534703531/(902961561600 x7) - ...} (este solamente es una aproximación. Ver nota (en inglés).) |

Funciones de Gamma Incompletas:
 (x, a) =
(x, a) = 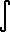
 e -t t(x-1) dt
e -t t(x-1) dt
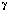 (x, a) =
(x, a) = 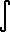
 e -t t(x-1) dt
e -t t(x-1) dt
 (x, a) +
(x, a) + 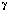 (x, a) =
(x, a) =  (x)
(x)