Math2.org Math Tables: Differentiation Identities
|
| (Math) |
Definitions of the Derivative:
![\[ \frac{df}{dx} = \lim<sub>h \to 0<sup>+</sup></sub> \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h} \] \[ \frac{df}{dx} = \lim<sub>h \to 0<sup>+</sup></sub> \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h} \]](/math/tex/f0390ff767f76f55d6184d800ecce60a.png) (right sided)
(right sided)
![\[ \frac{df}{dx} = \lim<sub>h \to 0<sup>-</sup></sub> \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h} \] \[ \frac{df}{dx} = \lim<sub>h \to 0<sup>-</sup></sub> \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h} \]](/math/tex/6fd4750664d426da5458bd41cfbf68f8.png) (left sided)
(left sided)
![\[ \frac{df}{dx} = \lim<sub>h \to 0</sub> \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h} \] \[ \frac{df}{dx} = \lim<sub>h \to 0</sub> \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h} \]](/math/tex/78b631e9d92bb3988ec8591f0eaf9ce7.png) (both sided)
(both sided)![\[ \frac{d}{dx} \int_a^x f(t) \, dt = f(x) \] \[ \frac{d}{dx} \int_a^x f(t) \, dt = f(x) \]](/math/tex/928d0a03d7d6f46f45a86c7fb5f810b5.png) (Fundamental Theorem for Derivatives)
(Fundamental Theorem for Derivatives)
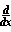 c f(x) = c
c f(x) = c 
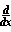 f(x) (c is a constant)
f(x) (c is a constant)
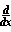 f(g(x)) =
f(g(x)) = 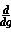 f(g) *
f(g) * 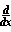 g(x) (chain rule)
g(x) (chain rule) 
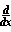 f(x)g(x) = f' (x)g(x) + f(x)g '(x) (product rule)
f(x)g(x) = f' (x)g(x) + f(x)g '(x) (product rule)
if f( x(r,s), y(r,s) )
if f( x(r,s) )
![\[ \frac{d}{dx} \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = \frac{f'(x)g(x) - f(x)g'(x)}{g(x)^2} \] \[ \frac{d}{dx} \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = \frac{f'(x)g(x) - f(x)g'(x)}{g(x)^2} \]](/math/tex/5fdc6c62e29eedc1d9cd33e8610ebee5.png) (quotient rule)
(quotient rule)
Partial Differentiation Identities
![\[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial r}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial r}
+ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y} \frac{\partial y}{\partial r}
\] \[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial r}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial r}
+ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y} \frac{\partial y}{\partial r}
\]](/math/tex/f3c4139f163f8d19c2e5571518f4ec67.png)
![\[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial s}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial s}
+ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y} \frac{\partial y}{\partial s}
\] \[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial s}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial s}
+ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y} \frac{\partial y}{\partial s}
\]](/math/tex/6c109268b5ee9eadfb8bbe3ced0a7d3f.png)
![\[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial r}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial r}
\] \[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial r}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial r}
\]](/math/tex/93a3de032496a4ea1b8fa9bdf965dcac.png)
![\[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial s}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial s}
\] \[ \frac{\partial f}{\partial s}
= \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial x}{\partial s}
\]](/math/tex/a223b91c15cdaae6f963f1615208df6f.png)
